Rotator cuff tear: Symptoms and effective treatment of a rotator cuff tear
Shoulder pain , limited mobility and loss of strength – these complaints are often caused by a so-called rotator cuff tear .
This is a tear in one or more tendons that stabilize the humeral head. The injury can occur suddenly or develop gradually over years in the joint.
At our specialized shoulder practice in Munich, we specialize in the diagnosis and treatment of rotator cuff tears and will accompany you on your journey back to pain-free movement.

What is the rotator cuff?
The rotator cuff consists of four muscles and their tendons that surround the shoulder joint. The tendons of the rotator cuff are:
Supraspinatus
Infraspinatus
Teres minor
Subscapularis
Together, they ensure the stability and mobility of the shoulder—especially when lifting and rotating the arm. In a rotator cuff tear , one or more of these tendons tear—either partially ( partial tear ) or completely ( complete damage ). Ruptures of the tendons of the supraspinatus and infraspinatus muscles are most common, followed by the subscapularis muscle, and least frequently, the teres minor muscle.
Causes: How does a rotator cuff tear occur?
A rotator cuff tear can have various causes. The most common causes of a rotator cuff tear include:
1. Degenerative (wear-related):
Over the years, tendon tissue loses elasticity and becomes more prone to tears. Small micro-injuries caused by wear and tear during overhead work, sports, or poor posture and restricted movement of the shoulder blade can, over time, degenerate into a tendon tear.
2. Traumatic (due to an accident):
A fall on an outstretched arm or an abrupt, jerky movement can cause sudden injury – often in younger or athletic people.
3. Secondary to other shoulder problems:
Impingement syndrome (narrowing under the shoulder roof) or calcification of the shoulder can place additional strain on the tissue and lead to a tendon rupture.

Shoulder pain and other common symptoms of a rotator cuff tear of the shoulder
The symptoms depend on whether the rupture occurred suddenly or gradually:
Pain during exertion , especially when lifting the arm, e.g. combing the hair
Night pain , especially when lying on the affected side
Loss of strength when lifting or turning the arm, e.g. carrying shopping bags
Restricted movement
Cracking or rubbing noises in the shoulder joint
In the case of an acute rupture, the pain can be very severe and mobility can be suddenly restricted.
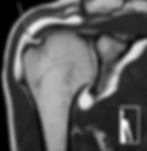
Diagnosis of a rotator cuff tear
The diagnosis of a rotator cuff tear can often be made clinically. At our practice, we perform a thorough clinical examination , specifically testing your shoulder's mobility, strength, and pain points.
Modern imaging techniques are used for further clarification:
Ultrasound – an ultrasound examination is suitable for a quick assessment directly in the practice
MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) – for precise visualization of the tendon tear, its size and possible accompanying injuries
X-ray – to assess the bony structures
Treatment of a rotator cuff tear: conservative or surgical?
The choice of therapy depends on the extent of the rupture, the age , the physical load and the individual limitations.
Conservative treatment for tendon rupture (rotator cuff tear)
Conservative therapy
For small or painless partial tears, surgery can often be avoided. The goal is to preserve shoulder function through targeted measures:
Physiotherapy to strengthen muscles and relieve tendon strain
Pain and inflammation relief through medication or injections
Daily adjustment to avoid further irritation
This form of therapy is particularly suitable for older patients or people with only minor functional impairments.

How long should I continue with conservative treatment and when is surgery recommended for a rotator cuff tendon tear?
Surgery is recommended if:
the complained symptoms persist despite therapy
the tendon is completely severed and its function is impaired
the shoulder is severely weakened
younger or active patients are affected
Surgical therapy
You should be prepared accordingly for the treatment of shoulder diseases and injuries as well as wear and tear of the cuff.
If the supraspinatus tendon is damaged or if several tendons of the rotator cuff show wear, the extremity will be immobilized for a short time after the procedure.
At the beginning, raising the arm only occurs as part of physiotherapy, passively or by using an exercise chair.
During the course of the treatment, muscle strengthening exercises are necessary to prepare the rotator cuff muscles and the joint for sporting activities.

How is the operation performed and how can I prepare for surgical treatment of the shoulder joint?
In most cases, the procedure is performed arthroscopically (keyhole surgery) . The torn shoulder tendon is repaired minimally invasively using small instruments during an arthroscopy , and the torn tendons are reattached to the bone . The goal of the operation is a rapid reduction in severe pain or pain in the shoulder area, improvement in mobility, and protection of the shoulder from subsequent damage. When there is a rotator cuff tear, damage to the long biceps tendon and tightness under the acromion are often treated in the same procedure to correct causes that could lead to a rotator cuff tear and improve the long-term prognosis of the shoulder.
In severe cases, reconstructive surgery of the shoulder joint or – in cases of very extensive damage – an artificial tendon transfer, a capsule reconstruction between the acetabulum and the humeral head, or an inverse shoulder prosthesis may be necessary.
Follow-up treatment, rehabilitation and recovery prospects of rotator cuff tears
After arthroscopic reconstruction, structured follow-up treatment is crucial. Typically, a rest period with immobilization begins. This can last from three to six weeks , followed by controlled physical therapy . Depending on the type of procedure, rehabilitation lasts between six and 12 months .
Physiotherapy treatment of the affected shoulder is important for the first six weeks after surgery. During this time, the shoulder is additionally moved passively using a CPM (continuous passive motion) chair.

Later on, independent training or exercises can supplement the therapy. Healing is monitored through regular checkups, including a manual shoulder examination and ultrasound examination.
With early diagnosis and consistent follow-up treatment, the chances of recovery are very good – many patients fully regain their shoulder function after rotator cuff reconstruction . Patients typically report that the stabbing pain they previously experienced was quickly relieved. In most cases, pain medication can be discontinued a few weeks after surgery.

Conclusion: Early therapy pays off
A rotator cuff tear is no small matter – if left untreated, it can lead to permanent movement restrictions in the shoulder area or shoulder arthrosis.
The sooner the right therapy is started, the better the chances of recovery.
At our shoulder practice in Munich, our orthopedic surgeon Prof. Ockert offers you individual, holistic care – from the initial consultation to complete recovery.
Do you have shoulder pain or trouble lifting your arm?
Make an appointment now with your shoulder specialist in Munich – we will help you competently and personally.

Questions about rotator cuff tears
When does a rotator cuff tear require surgery?
If the tear is large, there is severe pain, or mobility is severely restricted, surgery is usually recommended.
What surgical procedures are available for rotator cuff tears?
The rupture is usually sutured arthroscopically and the tendon is reattached to the bone.

How long does it take to heal after rotator cuff surgery?
The healing time is approximately 3–6 months, depending on the size of the tear and rehabilitation.
Can a rotator cuff tear be treated without surgery?
For small tears and minor discomfort, physiotherapy and pain therapy may be sufficient.

What are the risks of rotator cuff surgery?
As with any surgery, infections, bleeding, or re-tears are possible, but these rarely occur with standardized surgical techniques and highly experienced surgeons. Statistically, the greatest risk is that the sutured tendon fails to integrate with the bone or that it may tear again later.

PROF. DR. MED BEN OCKERT
Specialist in orthopedics and accident surgery, sports medicine.



